Despite being the largest employer in the world, the agriculture industry is also the least automated. However, the dwindling labor force coupled with the increasing strain on global food supply makes the agriculture industry the largest remaining opportunity for automation. Manufacturers are striving to commercialize connected and autonomous harvesting robots to help combat labor shortages, making the agriculture sector more mechanized in the process.
- FIGURE 1 attractive opportunities for players in the global precision harvesting market
Source: Secondary Sources, Primary Interviews, Related Research Publications, Press Releases, Industry Journals & Books, and MarketsandMarkets Analysis .
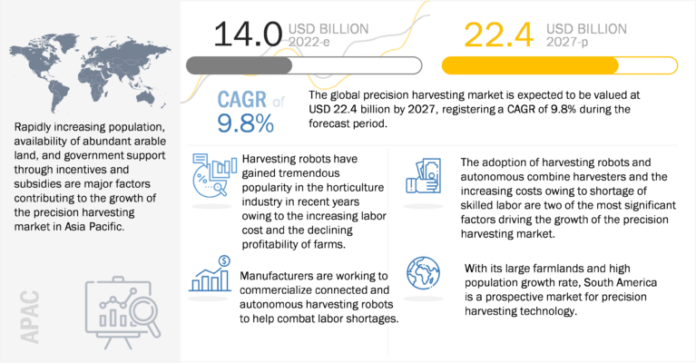
The precision harvesting market is expected to grow from USD 14.0 billion in 2022 to USD 22.4 billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 9.8%. The most significant factors driving the growth of the precision harvesting market include the increasing adoption of harvesting robots and autonomous combine harvesters, increasing labor costs owing to the shortage of skilled labor, and the increasing mechanization of farms in emerging countries in Asia Pacific and Africa. Precision harvesting has the potential to transform the agriculture sector, making traditional harvesting activities more efficient and economical. Increasing global food demand, extended profitability and crop yield, and minimum wastage of crops during harvesting are the other factors fueling the growth of the market. Governments in many countries are also helping farmers adopt advanced agricultural and technological tools to improve yield, further boosting the market
Increasing demand for harvesting robots in greenhouse and horticulture applications
Harvesting robots are mainly used in greenhouse and high-value crop cultivation applications as greenhouses have stable conditions that are friendlier to robotic harvesters, while the cultivation of high-value crops takes place outside standard growing seasons leading to a higher labor requirement, and thus a greater potential for using robotic harvesters.
The adoption of autonomous harvesting robots and connected devices is expected to increase in the coming years owing to the severe shortage of skilled labor in the horticulture industry and the continual demand for high-quality food. Various companies have developed robots to harvest tomatoes, raspberries, and sugar snap peas with minimal human intervention. For instance, Harvest Croo’s robotic harvesters are being tested in Florida; these harvesters employ vision sensors and software to scan plants and locate ripe berries using equipment advanced enough to avoid bruising or damaging the soft fruit. Similarly, Spain-based Agrobot has been testing a strawberry harvester in Driscoll’s berry field in Oxnard, California, while FFRobotics, an Israeli company, is testing its apple-picking technology in orchards in Washington. FFRobotics claims that its technology can precisely and gently pick 10 times more fruit than an average worker, helping growers reduce costs by supplementing or even replacing human pickers from the dwindling pool of harvesting laborers.
Increasing labor costs due to shortages coupled with the gradual reduction in hardware costs expected to push the adoption of harvesting robots in the coming decades
Technically an emerging technology, harvesting robots gained tremendous popularity in recent years owing to increasing labor costs in the horticulture industry and the declining profitability of farms. Unfortunately, the current technology is not affordable to most farmers—according to a survey by a US-based research agency, less than 3% of growers in the world currently use harvesting robots. However, the gradual reduction in hardware cost coupled with the shortage and steadily increasing cost of labor is set to increase the adoption of harvesting robots in the coming decades. Harvesting robots are being tested in Florida and California to pick strawberries and mechanize labor-intensive operations.
Precision harvesting technology to witness fastest adoption in regions with high labor shortage
Farming is a highly labor-intensive activity. Almost 50% to 70% of the production cost in horticulture is spent on labor—from harvesting to tasks performed before harvesting, such as weeding, fertilizer application, and site inspection. Automating these tasks is an extremely important step for large-scale farming operations to ensure profitability.
Precision harvesting technology improves production efficiency and enables the optimal use of resources, providing farmers additional bottom-line savings, especially in labor costs. As this has a direct impact on the profitability of farms, the demand for precision harvesting is increasing among farmers. Harvesters can perform various tasks, including automatic spraying, weeding, and pruning, besides harvesting. Air and ground robots equipped with sensors can be used to analyze farms and apply the collected data to instruct precision harvesting systems to perform required activities optimally. Such sensor-equipped harvesting robots are expected to gain tremendous popularity over the next 10 years, subsequently reducing labor costs and increasing the profitability of farms.
Precision harvesting is likely to make inroads fastest in areas where labor shortages for harvesting are maximum. Most harvesting robots are built for specialized tasks, like grapevine pruning, lettuce thinning, and strawberry picking. Corn and other commodity crops are already taking advantage of economies of scale to get ahead of the cost curve. Large farms in the US and Canada are buying self-steering tractors and self-propelled combined harvesters to save labor costs.
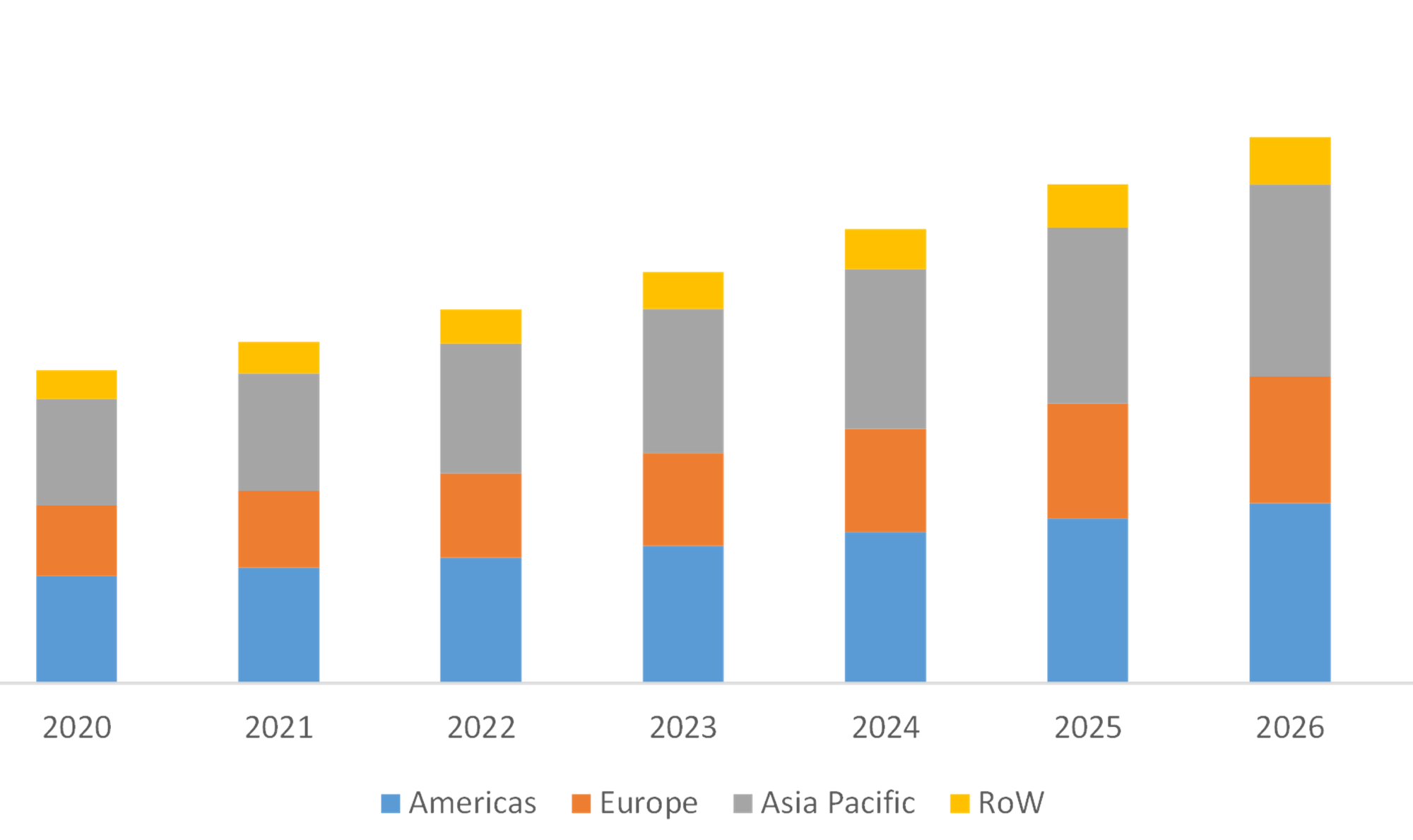
- FIGURE 2 global precision harvesting market, by region, (2020-2027)
Product launches, partnership/agreements, and mergers and acquisitions emerged as key growth strategies adopted by companies between 2018 and 2022
Players in the precision harvesting market implemented various strategies to uphold their position and ensure long-term growth and success. The precision harvesting market is competitive, with multiple players offering hardware, software, and services for agricultural applications. Product launches, expansions, partnerships, agreements, joint ventures, and mergers and acquisitions were key strategies adopted by major players in the precision harvesting market between January 2018 and July 2022; of these, product launches accounted for more than 50%. Companies adopted product launches to strengthen their product portfolios and cater to the needs of end users.
Major players operating in the precision harvesting market include Deere & Company (US); Trimble, Inc. (US); AGCO Corporation (US); AgJunction Inc. (US); Raven Industries, Inc. (US); AG Leader Technology (US), FFRobotics (Israel); Abundant Robotics, Inc. (US); Harvest Automation, Inc. (US); Harvest Croo Robotics (US); and Vision Robotics Corporation (US).








