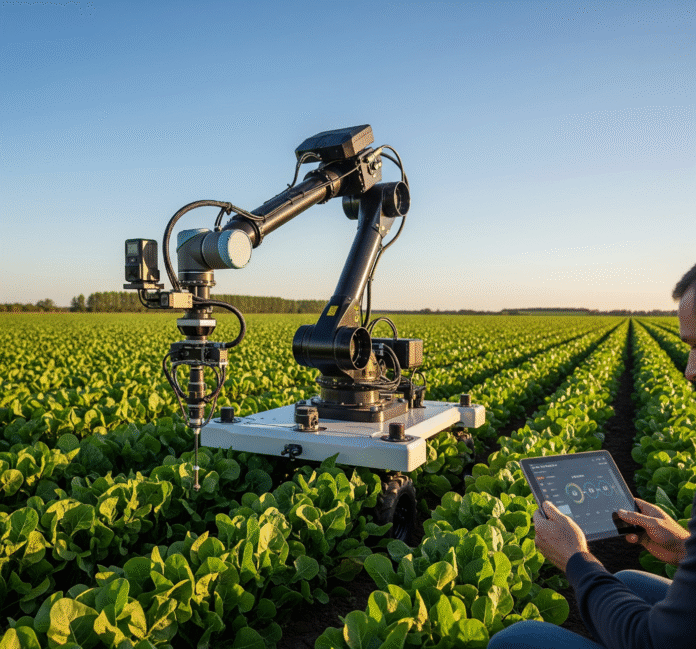
Agriculture has traditionally relied on experience, observation, and seasonal cycles. Farmers could assess weather patterns by looking at the horizon and determine soil conditions with a handful of earth. In recent years, however, these methods have been increasingly complemented, and in some cases transformed, by artificial intelligence (AI).
The AI in agriculture market, valued at USD 2.51 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 18.48 billion by 2033. According to ResearchIntelo, this reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.2% over the forecast period. This trend is driven not by novelty, but by the urgent demands of global food security, sustainability, and resource efficiency.
AI brings measurable precision to agricultural processes. It enables irrigation schedules to be optimized, pest outbreaks to be predicted in advance, and soil health to be monitored continuously. These capabilities are increasingly shaping the operational and strategic direction of farms worldwide.
Factors Driving AI Adoption in Agriculture
AI in agriculture is not a luxury reserved for technologically advanced facilities; it is becoming a necessity. Several structural and economic drivers are contributing to this shift.
- Rising Productivity Requirements
Global food demand is expected to grow substantially as the population approaches 9.7 billion by 2050. Meeting this demand with conventional practices risks overexploiting resources and degrading the environment. AI offers a path to higher yields with reduced inputs, including water, fertilizer, and labor.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The agricultural supply chain is under increasing pressure from climate variability, geopolitical tensions, and shifting trade dynamics. AI-powered forecasting tools provide yield estimates and risk assessments that enable supply chain adjustments in advance.
- Affordability of Digital Technologies
A decade ago, advanced agricultural tools such as drones and IoT-based monitoring systems were cost-prohibitive for many farms. Today, reduced hardware costs and the availability of cloud-based analytics have made AI more accessible to small and medium-sized operations.
- Government and Policy Support
Several countries have introduced targeted subsidies, technology adoption programs, and research collaborations to encourage AI integration in farming. These initiatives cover applications such as smart irrigation, AI-assisted crop disease detection, and soil condition monitoring.
- Growing Demand for Food Traceability
Regulatory and market demands for transparency in food sourcing are increasing. AI-powered tracking systems can monitor crops from planting through to retail distribution, ensuring greater accountability.
Market Segmentation
As per ResearchIntelo analysis, the AI in agriculture market comprises a diverse ecosystem of solutions and services.
By Component
- Software: Algorithms for predictive analytics, crop modeling, and farm management.
- Hardware: Includes drones, autonomous tractors, and environmental sensors.
- Services: Covers consulting, system integration, analytics, and maintenance.
By Technology
- Machine Learning: Enhances yield predictions, disease detection, and resource optimization.
- Computer Vision: Identifies plant stress and pest infestations from aerial or satellite imagery.
- Predictive Analytics: Models weather patterns, soil performance, and market demand.
- Robotics: Mechanizes labor-intensive tasks such as planting and harvesting.
- Others: Includes GIS mapping tools and automated irrigation systems.
By Application
- Precision Farming: Manages agricultural inputs at granular levels.
- Livestock Monitoring: Tracks animal health, movement, and feeding.
- Drone Analytics: Captures and processes aerial data.
- Agricultural Robots: Executes repetitive field operations.
- Crop Management: Oversees growth stages, nutrient needs, and pest control.
- Soil Management: Monitors moisture, nutrient composition, and compaction.
By Deployment Mode
- Cloud: Offers scalability and remote data processing where connectivity permits.
- On-Premises: Preferred in regions requiring local control over data.
By Farm Size
- Small & Medium Farms: Increasing adoption due to modular, cost-effective solutions.
- Large Farms: Maintain higher adoption rates owing to economies of scale.
Regional Overview
According to the report by ResearchIntelo, North America leads the market with an estimated USD 850 million in 2024. The United States and Canada are at the forefront in adopting precision irrigation systems and AI-driven crop analytics, supported by both private investment and public policy.
Asia Pacific is forecast to grow at the fastest pace, with a CAGR of 29.5%. The region’s adoption is driven by advancements in AI-enabled pest detection, data-based irrigation management, and government-supported technology adoption programs.
Europe exhibits steady growth, supported by regulatory frameworks that prioritize environmental sustainability. AI tools are being applied to meet emission reduction and biodiversity goals in addition to improving yields.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa represent emerging markets with notable potential. Infrastructure limitations remain a challenge, yet applications in precision irrigation and crop monitoring are gaining ground.
Emerging Opportunities
Several technological and market trends are poised to influence the AI in agriculture sector over the next decade.
- Integration with IoT, Blockchain, and 5G: Enables seamless communication between farm equipment, sensors, and data platforms, with blockchain ensuring traceability.
- Support for Sustainable and Organic Agriculture: AI facilitates compliance with organic standards while maintaining efficiency.
- Expansion of Rural Digital Infrastructure: Broader connectivity will make advanced AI tools accessible in remote regions.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture Initiatives: AI supports adaptive planting schedules and water conservation strategies in response to unpredictable weather patterns.
- Enhanced Food Quality Assurance: Automated quality assessment tools from field to packaging.
Challenges to Address
Despite rapid growth, AI adoption in agriculture faces several obstacles.
- High Capital Investment: Comprehensive AI systems still require significant financial outlays.
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity: Farmers are cautious about sharing operational data with external platforms.
- Limited Digital Literacy: The operation of AI tools requires specific skills that are not yet widespread in rural communities.
- System Complexity: Many AI solutions have steep learning curves.
- Resistance to Technological Change: Established practices can hinder the adoption of new technologies.
- Interoperability Limitations: Integration across different systems and platforms is often difficult.
Key Industry Participants
Prominent market participants include IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Deere & Company, Trimble Inc., Bayer AG, AGCO Corporation, Raven Industries, Prospera Technologies, Granular, and Taranis. These companies deliver not only software and hardware but also essential training, analytics, and after-sales support to facilitate AI adoption.
In addition to these large corporations, numerous startups are entering the market with specialized solutions such as AI-based pest detection, autonomous weeding, and soil health optimization.
Future Outlook
AI in agriculture is expected to transition from being an optional competitive advantage to a standard element of farming operations. The coming decade could see autonomous tractors, drone-based crop monitoring, and real-time soil analytics become routine features of agricultural management.
Adoption rates will vary depending on infrastructure availability, policy support, and the willingness of agricultural stakeholders to integrate AI into operations. However, as successful case studies continue to emerge, the momentum toward AI-enabled farming is likely to accelerate.
Conclusion
Agriculture has continually adapted to new tools and technologies, from mechanization to modern irrigation. AI represents the next major adaptation, with the potential to address pressing challenges in food production and sustainability. With market growth projected to reach USD 18.48 billion by 2033, the integration of AI into farming is set to become increasingly indispensable.
As per ResearchIntelo analysis, this trajectory reflects not only technological progress but also a fundamental reshaping of agricultural practices to meet the demands of a changing global landscape.
Source: https://researchintelo.com/report/ai-in-agriculture-market